Introduction
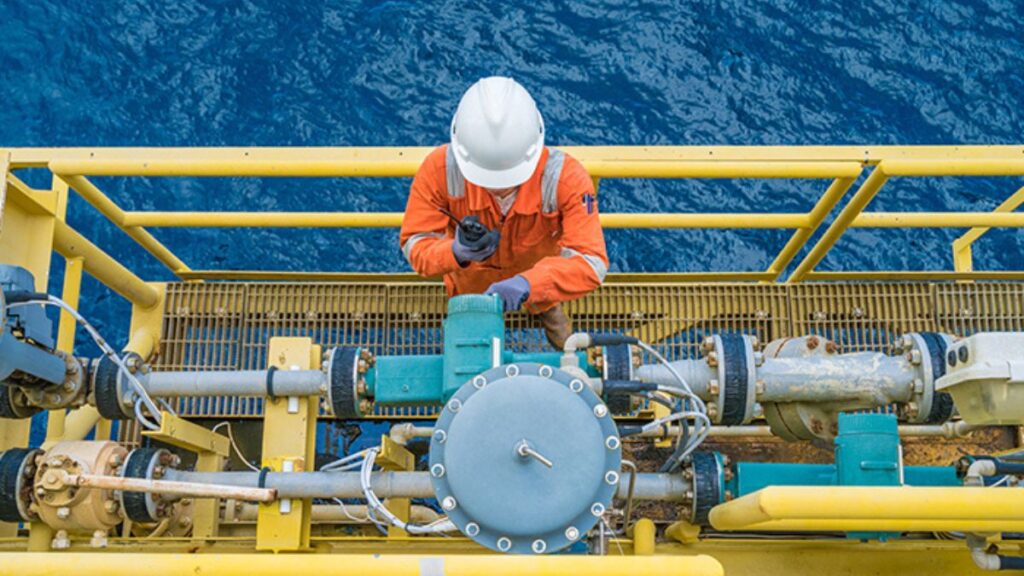
In the high-stakes world of oil and gas, reliability isn’t just a competitive advantage—it’s a necessity. The performance of every drilling or production site ultimately hinges on one critical factor: the ongoing health of its wells. Behind every barrel of oil or cubic foot of gas delivered to market lies a complex system that demands continuous care and oversight. As the industry evolves with new technologies and tighter regulations, well-maintenance has emerged as a strategic pillar, ensuring operations remain efficient, safe, and environmentally responsible. What follows is an in-depth examination of why maintenance is no longer a back-end task but a front-line priority that shapes the future of energy.
Well Maintenance: The Backbone of Oil and Gas Operations
The oil and gas industry thrives on the consistent performance and productivity of its wells. Well maintenance isn’t just a technical requirement—it’s the very foundation that sustains energy flows and keeps resources available for markets worldwide. When a well is actively maintained, its components work together seamlessly, minimizing unexpected failures and optimizing output for years beyond initial projections. Industry research shows that robust maintenance programs lead to increased well lifespan and higher return on investment, often resulting in up to a quarter more production compared to wells with sporadic or reactive care. Efficient, good care also shields organizations from the risks of regulatory non-compliance, environmental hazards, and public relations setbacks, all of which can spin into costly problems if neglected.
Resources such as renegadewls.com demonstrate how modern maintenance models go beyond the basics by incorporating state-of-the-art tools and data-driven procedures that enhance both safety and performance. By taking a comprehensive, forward-thinking approach to servicing wells, companies can catch issues before they escalate, such as early signs of corrosion, pressure drops, or equipment fatigue. Proactive servicing aligns well with global movements aiming at responsible resource management and environmental stewardship, further cementing well maintenance as an essential practice for any operator serious about maximizing efficiency and corporate sustainability.
Key Aspects of Effective Well Maintenance
An effective well-maintenance program hinges on a balanced combination of scheduled inspections, detailed monitoring, and timely interventions. Rather than waiting for something to go wrong, successful operators adopt a preventive maintenance mindset—one that relies on insight and planning instead of costly repairs in the aftermath of a breakdown. Key elements of this approach include routine checks for corrosion, structural weaknesses, production irregularities, and mechanical health of key well components. Every inspection not only extends the life of the well but also serves as an essential learning opportunity, revealing patterns that might otherwise go unnoticed and allowing teams to adapt their strategy as conditions change.
When operators can anticipate issues through trending and predictive analytics, they reduce not only downtime but also maintenance-associated costs. It’s common for robust programs to lead to substantial savings in both equipment and labor, helping companies stay competitive and compliant in a rapidly evolving marketplace.
Hidden Costs of Neglecting Well Servicing
The decision to delay or downplay well servicing often comes with a hidden price tag. At first glance, skipping an inspection or stretching out servicing intervals may seem like an easy way to cut operational expenses. However, these shortcuts can lead to cascading failures, ranging from minor equipment malfunctions to complete shutdowns of wells. Lost production isn’t always immediately visible—it can manifest as gradual declines in output or efficiency losses that add up to significant revenue shortfalls over time. More dramatic failures, such as unexpected blowouts or casing collapses, incur emergency response costs and can halt production for days, weeks, or even months.
Deferred servicing not only increases the risk of large-scale technical failures but can also result in non-compliance with regulatory mandates, which can lead to heavy fines and legal ramifications. Additionally, frequent breakdowns can damage a company’s reputation, making it more difficult to attract partners, investments, or new field personnel. In essence, maintenance shortcuts nearly always end up costing more financially and operationally.
The Link Between Well Health and Environmental Stewardship
Every well has the potential to impact the environment, but well-maintained operations can serve as a model for responsible resource management. Preventing leaks, spills, and emissions at their source is crucial for protecting water supplies, soil health, and air quality. Even minor leaks, if left unaddressed, can accumulate into serious environmental hazards over time. As regulations governing emissions and waste disposal become increasingly stringent, a clear commitment to well integrity also helps companies avoid penalties and costly remediation tasks while securing their operating permits.
The communities living near drilling and production sites are more likely to feel confident in an operator’s commitment to safety and sustainability when maintenance is transparent and robust. In addition, staying ahead of compliance thresholds often reduces insurance premiums and improves stakeholder relations, laying the groundwork for enduring partnerships and access to new markets.
Technological Innovations Transforming Well Maintenance
Technology plays a pivotal and expanding role in reshaping how wells are maintained across the oil and gas sector. The introduction of remote sensors, drones, and automated monitoring platforms has unlocked powerful capabilities for detection, diagnosis, and intervention, frequently with minimal human input. Real-time data streaming to centralized operations centers can enable the identification and addressing of even the slightest anomalies—such as subtle shifts in pressure or unexpected temperature spikes—long before they become costly problems.
Additionally, the rise of artificial intelligence and machine learning provides predictive insights, enabling maintenance teams to forecast component wear and schedule repairs or part replacements with pinpoint accuracy. The result is a maintenance process that is not only more efficient but also more preventative and less reactive. These technologies have driven a significant reduction in unplanned downtime, enabling companies to optimize resource allocation, save money, and enhance safety across every phase of a well’s lifecycle.
Building a Skilled Workforce for Long-Term Well Efficiency
Highly skilled and continuously trained field personnel are at the heart of any successful maintenance operation. The oil and gas industry is rapidly adopting new tools and processes, and workers must remain up to date on best practices, regulatory changes, and the capabilities of cutting-edge technology. Routine training, professional certifications, and cross-functional teamwork foster a vigilant and adaptable workforce that is prepared to address any maintenance challenge.
Collaboration is a central ingredient for success: engineers, operators, and service partners must communicate effectively to maximize shared knowledge and leverage each other’s expertise. Facilities that cultivate this team-based approach to well care almost always enjoy fewer incidents, more innovative problem-solving, and higher morale among staff—factors that directly translate to better well efficiency and stronger business outcomes.
Future Trends: Sustainability and Enhanced Recovery Techniques
The drive toward cleaner energy and global decarbonization efforts is reshaping maintenance expectations and approaches throughout the oil and gas ecosystem. Well health is a significant enabler of sustainability initiatives—helping operators get more out of every barrel while reducing waste and resource inputs. New strategies, such as enhanced oil recovery (EOR), hinge on a foundation of solid, reliable, and well-integrity, as EOR methods rely on stable operating environments for optimal results.
Proactive maintenance directly supports these advanced techniques, enabling more efficient chemical, water, or gas injections. As asset integrity becomes increasingly essential in achieving net-zero goals and minimizing the environmental footprint of energy production, the role of well care will only become more prominent in the years ahead.
Practical Steps for Operators to Boost Maintenance Programs
While the journey toward optimal healthy maintenance requires investment, the rewards are considerable, both in cost savings and operational stability. Building a robust program starts with digitizing asset management, ensuring every small detail is recorded and analyzed for early warning signs. Operators benefit from developing tailored inspection checklists suited for each well’s age, geography, and production profile.
- Digitize records for all assets and maintenance logs to enhance traceability and gain valuable insights.
- Conduct recurring, standardized inspections based on each well’s history and known risk factors.
- Set up communication channels between teams to facilitate trend analysis and incident reporting.
- Commit to upskilling staff on emerging technologies and regulatory developments.
- Hire outside experts for specialized interventions or when encountering complex well conditions.
Operators who put these principles into action routinely experience fewer interruptions, improved production, and a reduction in both repair expenses and environmental liabilities. Ultimately, a culture that values ongoing well health invests in the future, ensuring the oil and gas sector remains efficient, responsible, and resilient in a rapidly evolving industry landscape.