Landscaping is increasingly moving toward approaches that prioritize environmental responsibility and long-term sustainability. More homeowners and designers are considering ways to create outdoor spaces that conserve water, support local ecosystems, and use materials with minimal environmental impact. Practices such as planting native species, reducing chemical inputs, and incorporating efficient irrigation are becoming common strategies for balancing beauty with ecological care.
Observations from organizations like My Sons Landscape reflect these broader trends, showing how sustainable methods are shaping modern outdoor design. Simple choices, such as selecting climate-appropriate plants or managing soil health, can make a meaningful difference. By focusing on environmentally conscious decisions, outdoor spaces can become more resilient, functional, and harmonious with the natural surroundings, while still providing enjoyable areas for daily use.
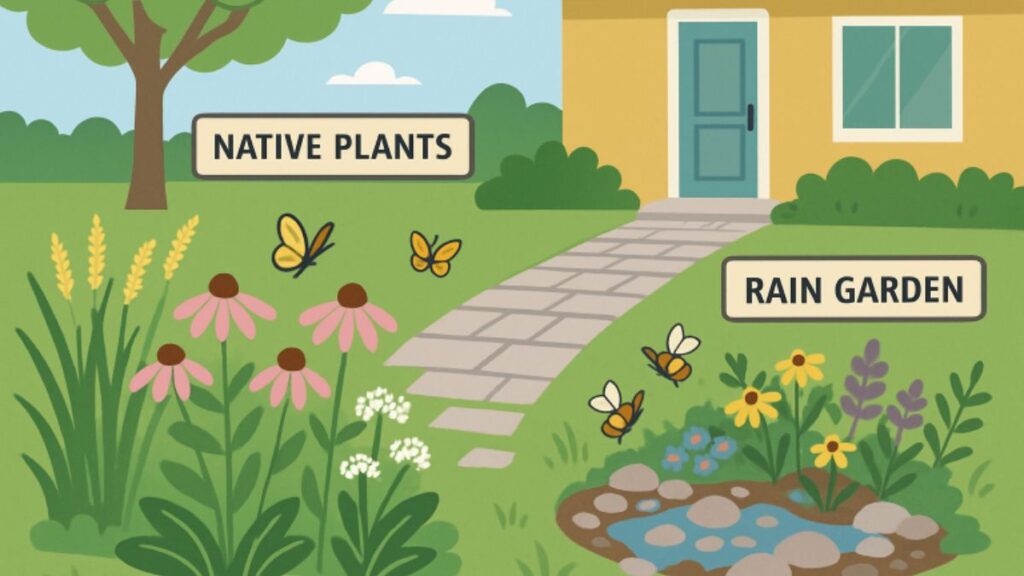
Embracing Native and Drought-Tolerant Plants
Opting for native, drought-resistant plants is essential for sustainable landscaping. These plants have adapted to local conditions, requiring less irrigation and fertilizer. They also help sustain local wildlife like birds, pollinators, and beneficial insects. Drought-resistant species, often native, endure with minimal water, keeping gardens vibrant through dry periods. They contribute to low-maintenance, colorful outdoor areas that adjust to climate changes. Designers often incorporate rain gardens and prairie wildflowers to create spaces that are both beautiful and ecological.
Smart Water Management Techniques
Water conservation is essential for sustainable landscaping. Traditional lawns and exotic plants often demand extensive irrigation, putting pressure on water resources, especially in drought-affected regions. Sustainable techniques focus on capturing rainfall and enhancing irrigation efficiency. Rain gardens collect runoff from roofs and paved surfaces, filtering pollutants and replenishing groundwater. Smart controllers use weather data and soil sensors to water only when necessary, reducing wastage. Rain barrels and catchment systems harvest runoff for later use, helping gardens thrive with less potable water. Drip irrigation delivers water directly to roots, minimizing evaporation. These approaches enable landscapes to flourish while conserving water, protecting financial resources and the environment, and preventing erosion or flooding during hot, dry summers.
Organic Lawn Care Practices
Organic lawn care emphasizes “do no harm” to soil, water, and garden visitors. It replaces synthetic fertilizers and pesticides with natural amendments like compost and mulch, which enhance soil health, conserve water, and promote deep root growth. Techniques such as natural pest control, crop rotation, aeration, overseeding, and choosing hardy grass varieties improve lawn vitality. This comprehensive approach increases resistance to diseases, pests, and droughts with minimal intervention. It also stimulates microbial activity that aids nutrient recycling. Many municipalities advocate for or enforce reduced chemical use, as studies indicate organic practices benefit water quality and pollinator safety.
Designing Multifunctional Outdoor Spaces
Contemporary landscape design balances function and form. Today’s outdoor spaces act as extensions of the home, offering relaxation, socializing, recreation, and productivity. Creative solutions like modular furniture, shade structures, outdoor kitchens, fire pits, and water features cater to versatility. Families can turn yards into productive areas with vegetable patches, play zones, and herb gardens. Zoning with natural screens or subtle grade changes creates outdoor rooms. Edible gardens and pollinator habitats serve as both functional spaces and visual delights, with seasonal harvests and vibrant colors. These landscapes improve the quality of life and encourage outdoor time, deepening the connection with nature.
Integrating Sustainable Hardscaping Materials
The push toward sustainability extends beyond plants to the foundational elements used in landscaping. Modern landscape architects replace resource-heavy hardscape materials with recycled, salvaged, or manufactured options that are environmentally responsible. Permeable pavers let rainwater soak in, reducing runoff, urban heat, and flooding. Reclaimed wood, recycled plastic composite decking, and low-impact sourced natural stone cut carbon emissions and raw material extraction. These materials complement native gardens and boost site sustainability. For instance, deconstructed metalwork and broken concrete (“urbanite”) add texture and durability, assist rainwater infiltration, and reduce waste. The mix of industrial and organic elements creates visually pleasing, environmentally friendly landscapes that balance utility and beauty.
Conclusion
The rapid evolution of sustainable landscaping is not simply about staying current with the latest design trends; it is a tangible way to address pressing environmental challenges at home. By choosing native plants, practicing mindful water management, committing to organic care, and selecting eco-conscious materials, property owners are joining a movement that values both individual well-being and the preservation of our shared resources. Every landscape, from a cozy backyard to a sprawling commercial property, holds the power to sequester carbon, filter water, shelter wildlife, and delight the senses. Embracing sustainable practices means transforming these outdoor spaces into sanctuaries that serve the greater good, not just for today, but for generations to follow. In the end, developing gardens with ecological integrity is less about sacrificing beauty and more about discovering new, deeper kinds of beauty and purpose that benefit everyone.