As environmental awareness grows, the homebuilding industry is embracing sustainable practices to meet the demands of eco-conscious buyers. Vantage Homes Corp., a leading builder in Colorado Springs since 1983, exemplifies this commitment by integrating eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient designs into its customizable homes. Serving communities like Flying Horse, Home Place Ranch, and Wolf Ranch, Vantage Homes offers a range of floor plans that reflect modern living while prioritizing sustainability.
Eco-Friendly Materials
Modern builders are increasingly selecting materials that minimize environmental impact. Options like bamboo, recycled steel, and reclaimed wood are popular for their sustainability and durability. For instance, bamboo grows rapidly and absorbs more CO₂ than traditional timber, making it an excellent renewable resource. Additionally, using low-VOC paints and finishes improves indoor air quality, promoting healthier living environments.
Energy-Efficient Designs
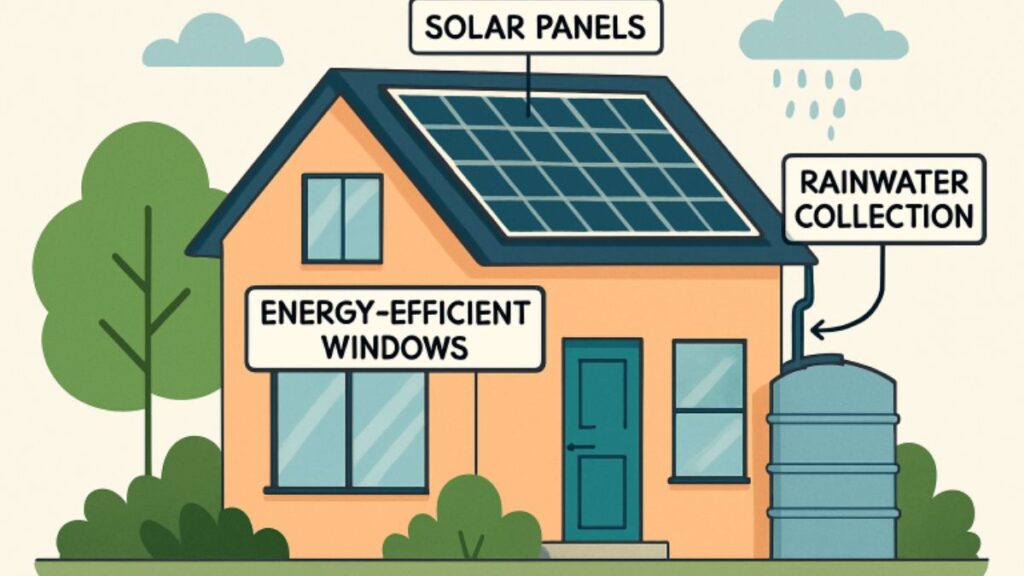
Energy efficiency is a cornerstone of sustainable homebuilding. Incorporating passive solar design, high-performance insulation, and energy-efficient windows reduces reliance on artificial heating and cooling. The trend toward net-zero energy homes, structures that produce as much energy as they consume, is gaining momentum, with governments offering incentives for such constructions. Building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV), where solar panels are seamlessly incorporated into building materials, are becoming more prevalent, enhancing both aesthetics and functionality.
Water Conservation Strategies
With water scarcity becoming a global concern, sustainable homes are designed to use water more efficiently. Rainwater harvesting systems, greywater recycling, and low-flow plumbing fixtures are being integrated into residential construction to reduce dependence on municipal water supplies. Smart water management systems monitor usage, detect leaks, and provide homeowners with real-time feedback. Landscaping choices are also evolving, with drought-resistant plants and permeable paving helping reduce water consumption while maintaining attractive outdoor spaces.
Smart Home Technologies
Integrating smart technologies enhances a home’s sustainability by optimizing energy and water use. Smart thermostats, lighting systems, and appliances enable homeowners to monitor and control consumption remotely, resulting in significant energy savings. Advanced home automation systems can adjust settings based on occupancy and weather conditions, ensuring resources are used efficiently without sacrificing comfort.
Modular and Prefabricated Construction
Modular and prefabricated construction methods are gaining momentum as sustainable alternatives to traditional building techniques. Factory-built components reduce material waste, improve quality control, and shorten construction timelines. Because these elements are produced in controlled environments, they often achieve higher energy-efficiency standards than site-built structures. In 2026, modular construction is increasingly associated with sustainability, offering faster project completion, reduced site disruption, and lower overall environmental impact—without compromising design flexibility or comfort.
Biophilic Design
Biophilic design emphasizes the connection between humans and nature, incorporating natural elements into the built environment. Features like green roofs, living walls, and ample natural light create spaces that promote well-being and reduce stress. This design approach not only enhances aesthetics but also improves air quality and energy efficiency. The trend reflects a broader movement toward architecture that supports environmental responsibility, well-being, ethical decision-making, and emotional connectivity, all of which signal a shift toward more thoughtful, human-centered design.
Climate-Resilient Construction
With the increasing frequency of extreme weather events, building homes that can withstand such conditions is crucial. Climate-resilient construction involves using materials and designs that enhance durability and safety. For example, fire-resistant siding, impact-resistant windows, and reinforced foundations help protect homes from natural disasters. These measures not only safeguard occupants but also reduce long-term maintenance costs and insurance premiums.
Final Thoughts
The shift toward sustainable homebuilding reflects a growing commitment to environmental stewardship and resource efficiency. By embracing eco-friendly materials, energy-efficient designs, water conservation strategies, smart technologies, modular construction, biophilic design, and climate resilience, the industry is paving the way for a greener future. Homebuyers and builders alike are recognizing that sustainable practices not only benefit the planet but also enhance quality of life and long-term cost savings.