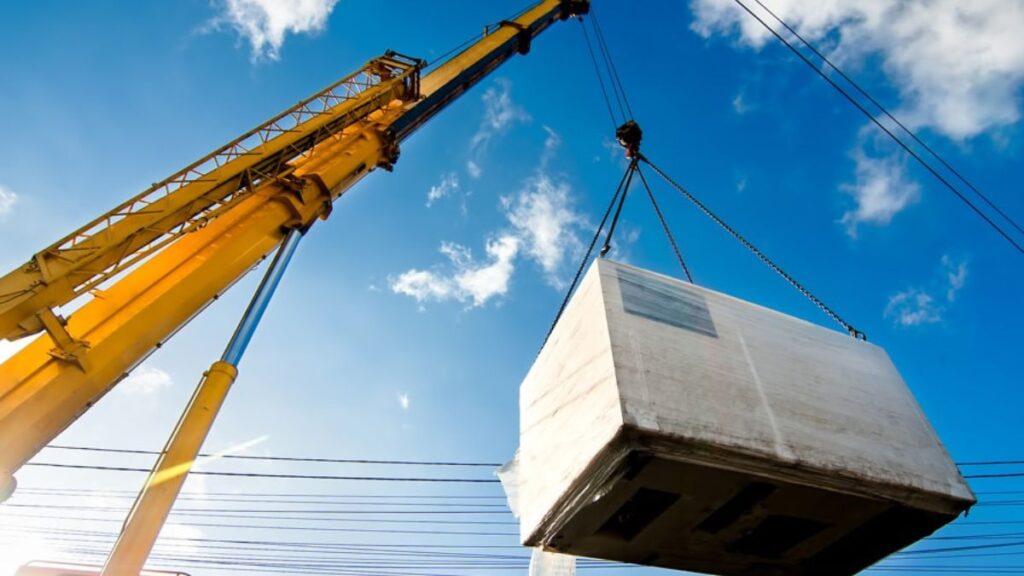
Safety in rigging operations has never been more critical in today’s industrial and construction environments. As projects grow in complexity and scale, a safety-first approach ensures protection for workers, reduces downtime, and keeps costs under control. Investing in resources like rigging safety training Tulsa can be a pivotal step for any organization seeking to enhance its safety standards and mitigate risk.
As workplaces evolve, safety methods and technologies advance. Implementing current protocols, proper training, and new tech helps maintain compliance and fosters a safety-focused culture. Monitoring equipment, staying alert to hazards, and effective communication are key to safe rigging. This guide covers these areas and practical applications, regardless of size or sector. Using recognized protocols and trusted resources enhances efficiency and protects workers. Follow these best practices to keep rigging operations productive and safe.
Regular Equipment Inspection
Before starting any lift or move, it is essential to conduct a thorough inspection of all rigging equipment. This includes checking slings, hooks, shackles, and lifting devices for signs of wear, cracks, deformation, or corrosion. Small issues—such as a frayed sling or bent hook—can escalate into major hazards if left unchecked. Implementing a rigorous inspection schedule helps identify and remove compromised gear from service, drastically lowering the risk of failure or accidents on site.
Inspection protocols should be standardized in accordance with OSHA and other relevant regulatory bodies, enabling teams to recognize when equipment does not meet minimum requirements easily. Documentation of inspections and prompt reporting of defects further strengthen the safety chain, ensuring no detail is overlooked.
Comprehensive Training Programs
Effective rigging safety hinges on the competence of every individual involved. Structured, hands-on training teaches workers how to handle equipment, recognize hazards, respond to emergencies, and execute safe lifting techniques. Programs should extend beyond classroom theory to include real-world scenarios, practical demonstrations, and ongoing refresher courses.
When workers understand not just the “how,” but the “why” behind safety procedures, compliance and vigilance increase. Organizations should actively encourage workers to stay up-to-date with evolving safety guidelines by utilizing trusted resources, such as the construction safety tips from the University of Minnesota.
Effective Communication Protocols
Every successful rigging operation relies on rock-solid communication. It’s not enough to merely inform team members of their roles—communication must be clear, concise, and confirmed. Standardized hand signals, pre-job safety briefings, and designated spotters ensure that everyone operates from the same playbook during lifts.
Utilizing two-way radios or other communication devices keeps team members in constant contact, allowing for quick adjustments when unexpected issues arise. Clear, confirmed signals reduce the risk of misunderstandings, which are among the leading causes of rigging-related incidents.
Proper Load Management
Load management is far more than simply picking up and moving weight. The center of gravity, type of load, and environmental conditions all dictate the correct rigging method to use. Failing to ensure a balanced load or using the wrong sling or hitch configuration can result in tip-overs, dropped loads, and even structural collapses.
Key Load Management Tips:
- Calculate load weights before making any lift.
- Use tag lines where necessary to guide loads safely.
- Double-check sling angles and secure connections at all points.
- Never exceed the rated capacity of rigging gear.
Comprehensive load management practices not only protect individuals but also keep machinery and structures free from costly damage.
Leveraging Technological Advancements
The arrival of advanced technology has brought a new dimension of safety and precision to rigging. Internet of Things (IoT) sensors can now provide real-time feedback on load stress, equipment status, and environmental conditions. Such tools enable crews to make instant, informed decisions and to proactively maintain rigging components before failures occur.
Automated monitoring, paired with digital record-keeping, creates a transparent safety system where the condition of every asset is readily visible at a glance. As these technologies advance, integrating them into rigging protocols can dramatically reduce human error and enhance workplace safety.
Ergonomics in Rigging Operations
Workplace injuries are not limited to catastrophic failures—musculoskeletal issues are a leading cause of lost time and worker discomfort. Ergonomic practices, such as using proper lifting techniques and utilizing mechanical aids, reduce strain and injury risks for workers handling heavy equipment or performing repetitive tasks.
Providing regular breaks, encouraging stretching, and investing in ergonomic tools help keep teams alert and fit for duty throughout the workday. Prioritizing ergonomics in rigging increases productivity and enhances long-term workforce health, as recommended by experts in occupational health.
Adherence to Regulatory Standards
Strict industry standards and regulations govern all rigging operations. Staying informed about updates from organizations such as OSHA ensures ongoing compliance and reduces the risk of legal or financial penalties. Reviewing site procedures regularly and conducting periodic audits are best practices for verifying that established guidelines are being followed and that all safety documentation is up to date.
Organizations that foster a culture of compliance often go beyond meeting minimum requirements, embedding safety into their operational DNA and leading the industry by example.
Conclusion
Adopting best practices in inspection, training, communication, load management, technology integration, ergonomics, and regulatory compliance is crucial for any organization seeking to maintain a safe workforce and ensure its operations run smoothly. By making safety a core value—supported by robust training and advanced tools—workplaces can confidently navigate the complex world of modern rigging and build a reputation for reliability and care.